Tell me, mum, who is actually allowed to control playgrounds?
If we looked on the Internet at "www.frag-mutti.de", we would probably not get ....


YOUR FORUM FOR PLAY, SPORTS UND LEISURE AREAS
We know from crash tests that the severity of an injury does not always correlate with the maximum strain at the measuring point, hence for example with the impact-induced acceleration of the head. In order to be able to describe, and above all compare, correlations between strain and induced injury nevertheless, derived variables were defined. One of these variables is the Head Injury Criterion.
The Head Injury Criterion (HIC, in German literature sometimes also referred to as HIC value, head injury factor or head performance criterion) is a criterion to assess head injuries ensuing from road traffic accidents. For instance, this non-dimensional value enables you to compare passenger safety of various vehicle models. It is the standardized integral value of the head acceleration. Depending on the observed time interval – 15 or 36 ms -, often the HIC15 or HIC36 value is given for a more precise distinction. The Head Injury Criterion is calculated as follows:
The gravitational acceleration is the acceleration of free fall and is also referred to as gravity of Earth. It indicates the acceleration of a body falling freely in a vacuum near the surface of the Earth in the Earth’s gravitational field. The average value of g at the Earth’s surface is 9.81 m/s2, however it varies regionally in the range of a few thousandths due to centrifugal force, oblateness of the Earth and altitude. The standard value of g is, by international definition, 9.80665 m/s2.
Today, the Head Injury Criterion is measured under standardized conditions. For all tests, the HIC threshold value is 1,000. A comparison with actual injuries showed that at this threshold value an injury graded 3 on the Abbreviated Injury Scale (AIS) will occur with a 0.5 (50%) probability. A grade 3 injury means a serious injury, for example a cerebral concussion with unconsciousness of less than 1 hour or the loss of an eye. If the HIC is 800, there is a 0.9 probability of getting less seriously injured. A HIC value of 1,300 means, conversely, that in 55 per cent of cases an even more serious injury will occur. An impact velocity producing head acceleration of 60g will develop a HIC36 of 1,000.
The HIC value is not only used to assess vehicle safety but also to assess the severity of a head injury. Hence, this measuring method is also used to determine the critical fall height of shock-absorbing playground surfacing and is described in the DIN EN 1177:2008 standard. The critical fall height is the maximum height of free fall, for which the playground surface provides an acceptable level of impact attenuation.
Test specimens or installed areas of the impact-absorbing surfacing materials under test are tested by being struck by an instrumented headform in a defined series of impacts from different drop heights. The signal emitted by an accelerometer in the headform during each impact is processed to yield the severity of the injury from the measured impact energy, defined as head injury criterion.
The HIC value of each impact is recorded and the critical fall height is determined as the minimum fall height at which the HIC value equals 1,000. The suitable shock-absorbing surfacing material is then selected depending on the playground equipment provided and its free height of fall.
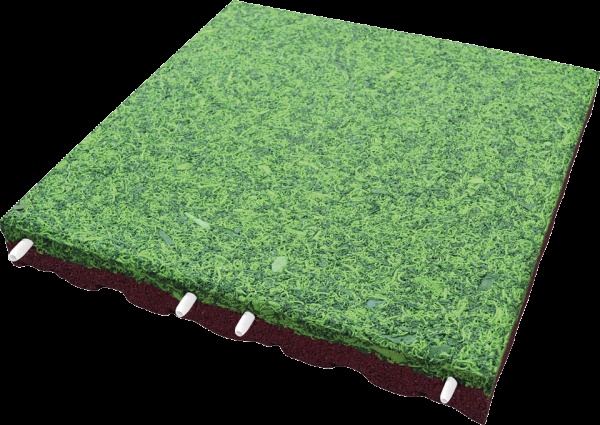
Adapted to the wide variety of different pieces of outdoor and indoor playground equipment, the Kraiburg Relastec GmbH & Co. KG, for example, provides suitable impact protection slabs for fall heights ranging from 0.60 to 3.0 metres. All products made of bonded, permanently elastic recycled rubber granules bear the GS safety certification mark by TÜV SÜD in compliance with DIN EN 1177:2008.
Aside from the safety aspect, of course, an appealing appearance and ease of installation also play an important role with all Euroflex® products.
Therefore the Kraiburg Relastec GmbH & Co. KG constantly extends its product range to meet the growing demands. Apart from the numerous variants of EPDM granules, the new product range of EPDM mulch slabs is a line that looks like natural bark mulch or grass. All products are certified and tested for PAH content according to the latest AFPS GS 2014:01 standard.
In order to cater for the cross-generational play concept, special play systems such as Ludo, Chess and Draughts/ Nine Men’s Morris were designed, which can be used both indoors and outdoors.
For further information, please visit www.kraiburg-relastec.com/euroflex.
Photo: Kraiburg